polarimeter in water|polarimetry pdf : discount store Figure 3a–e illustrate the behaviour of the polarimeter during a blank measurement with ultra-pure water in the 5-cm optical cell. Figure 3a shows scaled and normalised optical signals measured .
Resultado da The latest tweets from @ellieleen
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Resultados da Mega Sena: Ano 2004. Veja todos os resultados da Mega Sena do ano 2004 abaixo. Os números vencedores são exibidos em ordem de data para cada sorteio que acontece durante o ano. Selecione qualquer sorteio para saber mais informações. Para os resultados de um ano .
Chemists use polarimeters to investigate the influence of compounds (in the sample cell) on plane polarized light. Samples composed only of achiral molecules (e.g. water or hexane), have no effect on the polarized light beam.When plane-polarised light passes through some crystals, the velocity of left-polarized light is different from that of the right-polarized light, thus the crystals are said to have two refractive indices, i.e. double refracting. Construction: The polarimeter consists of a monochromatic source S which is placed at focal point of a convex lens L. Just after the convex lens there is a N. A sample containing a single enantiomer of fluoxetine (Prozac) is placed in a polarimeter. The observed rotation is 9.06° clockwise. The sample was made by dissolving 1.24 g of fluoxetine in a solution with a total volume of .Turn on the polarimeter and allow it to warm up for 30 minutes. Fill the polarimeter cell with a solvent that has a known specific rotation value. Place the cell in the polarimeter and adjust the polarimeter until the reading matches .
An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with .
Figure 3a–e illustrate the behaviour of the polarimeter during a blank measurement with ultra-pure water in the 5-cm optical cell. Figure 3a shows scaled and normalised optical signals measured .A polarimeter refers to an optical instrument used to determine the polarization properties of light beams and samples. It consists of a polarization generator and analyzer, which produce and analyze a beam of known polarization state. . if it is dissolved in an optically inactive liquid like water, the degrees of angle of rotation depend .This polarimeter comes standard with two wavelengths: 589nm and 546nm and will pass an FDA inspection with the appropriate water bath to control temperature or with optional Temptrol™ Electronic Heating and Cooling. IQOQ documentation is included with the instrument. Proper preparation ensures the accuracy of polarimeter readings. This involves checking the instrument’s calibration and preparing the sample correctly. Steps for Preparing the Polarimeter: Calibration: Make sure the polarimeter is calibrated with a known standard, like pure water, which should show zero optical rotation.
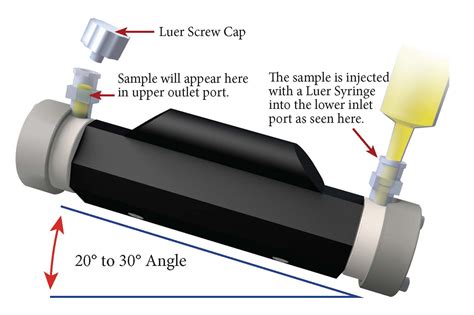
1. Clean the polarimeter tube, beaker, flask and measuring cylinder with water. 2. Fill the polarimeter tube with distilled water. As you rotate the analyzer through 3600, you observe four uniform illumination positions- two of these are weak in intensity and the other two are strong. Choose one of the weak Cleaning procedure of Polarimeter: The Analyst shall clean the Polarimeter and its surrounding with the dry cloth before and after use. If the solution spills on the instrument then clean it immediately with the dry cloth. If required clean the instrument with approved detergent (e.g. 1% Hemtop) followed by purified water and wipe with the dry . To address the problem of water surface detection imaging equipment being susceptible to water surface glints, this study demonstrates a method called De-Glints for suppressing glints and obtaining clear underwater images using a division of focal plane (DoFP) polarimeter. Based on the principle of polarization imaging, the best polarization angle and .2. Standard value of specific rotation of water o = 66.5 . 3. Standard value of specific rotation of Glucose (Solvent water) = 52o. Precautions and Source of Error: 1. The polarimeter tube should be well cleaned. 2. Water and sugar used should be dust free. 3. Whenever a solution is changed, risen the tube will new solution under concentration or
charpy impact test curve
Polarimetry is a technique used to measure the rotation of polarized light as it passes through a sample. . It can be used to determine if a product has been adulterated with a cheaper ingredient or if it has been diluted with water. Biomedical research: Polarimetry is used in biomedical research to study the structure and properties of . Principles of Polarimetry. Polarimetry measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid. The measured rotation can be used to calculate the value of solution concentrations; especially substances such as sugars, peptides and volatile oils. A polarimeter consists of a polarized light source, an analyzer, a graduated circle to measure .In this study, the dynamic adaptation capability of the DoFP polarimeter is utilized to study the automatic suppression method of water surface glints in water environmental observation. Section 2 of the paper presents a novel polarization-based suppression method for a DoFP polarimeter based on a Stokes vector polarization imaging model.
Malic Acid. Harry G. Brittain, in Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances and Excipients, 2001 4.2.1 AOAC Method 968.19. Application of the method requires access to a polarimeter having accuracy to at least 0.01°, and which is equipped with a sodium vapor lamp operating at 589 nm.. The (L)-malic acid Stock Solution (10 mg/mL) is prepared by placing 1.0 g of reference .Polarimeters can be used in kinetics experiments to follow the change in concentration of an optically active sample as a reaction proceeds. Sugars are common examples of optically active compounds. Sucrose is a disaccharide . A pure sample of the naturally-occurring, chiral compound A (0.250 g) is dissolved in acetone (2.0 mL) and the solution is placed in a 0.5 dm cell. Three polarimetry readings are recorded with the sample: 0.775 o, 0.806 o, 0.682 o. What is [a]? What would be the [a] value of the opposite enantiomer? Answer. TBA
polarimetry. An example of an optically active molecule is a sugar. Water and other common solvents are not optically active and so when solutions are prepared, it is the dissolved optically active chemical (e.g. the sugar in water) that causes the rotation, not the solvent. Rotation and Specific Rotation
Apparatus Used: Polarimeter, a balance, measuring cylinder, beaker and a source of light. (Sodium lamp for half shade polarimeter and ordinary bulb or mercury lamp for biquartz polarimeter.) Formula Used: The specific rotation of the plane of polarization of sugar dissolved in water can beA polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to determine the angle of rotation caused by an optically active material moving through polarized light. As the angle of rotation is defined, the degree by which the light is rotated. Basically, the angle of . Glucose is a chiral molecule, whereas water is not. A solution of chiral molecules can consist of all left-handed molecules, all-right-handed molecules, or a mixture of both kinds. . you will make a homemade polarimeter. A polarimeter is a scientific instrument that precisely measures the angle of polarization and the brightness of light .Polarimetry is the measurement of optical rotation of substances by using a polarimeter. A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light.
The CCD cameras employed in optical polarimetry can be roughly divided into two classes: smaller units with the thermoelectric cooling and pixel area up to about 2048 × 2048 (used mostly for broadband polarimetry) and large pixel area (or mosaic) units with cryogenic cooling (used for spectropolarimetry, imaging polarimetry and in multi .Place the water sample into the polarimeter. In order to determine the angle of rotation for a sample, a reference sample must be used, comparable to taring a balance to define the zero point or zeroing spectrophotometer against a blank solution. Water is a suitable blank for this lab. Place the water sample in the polarimeter.The “normal sugar solution” is defined as 26.016 g of sucrose dissolved in water at 20 °C to a final volume of 100 ml. Similar to the Brix scale for sugar level, temperature control is important and is included in all Schmidt + Haensch polarimeters.You can count on reliable measurements of the International Sugar Scale Degree Z (°Z) with .
polarimetry sample
polarimetry pdf
A pure sample of the naturally-occurring, chiral compound A (0.250 g) is dissolved in acetone (2.0 mL) and the solution is placed in a 0.5 dm cell. Three polarimetry readings are recorded with the sample: 0.775 o, 0.806 o, 0.682 o. What is [a]? What would be the [a] value of the opposite enantiomer? Answer. TBA A small pump is used to circulate the water. The imaging polarimeter is out of view but situated directly below the tank pointed upward. Full size image. Static scenes Indoor environment.
charpy impact test cvn
Aprenda a tocar a cifra de Sutilmente (Nando Reis) no Cifra .
polarimeter in water|polarimetry pdf